
The gallbladder is a small organ in your upper right abdomen which lies beneath the liver and is connected to the bile duct. It stores bile, a yellowish liquid produced by the liver that helps your body digest oily and fatty food.
Before a meal, the gallbladder may be filled with bile and is about the size of a small pear. During and after meals, the gallbladder squeezes the stored bile into the small intestine through a tube called the common bile duct.

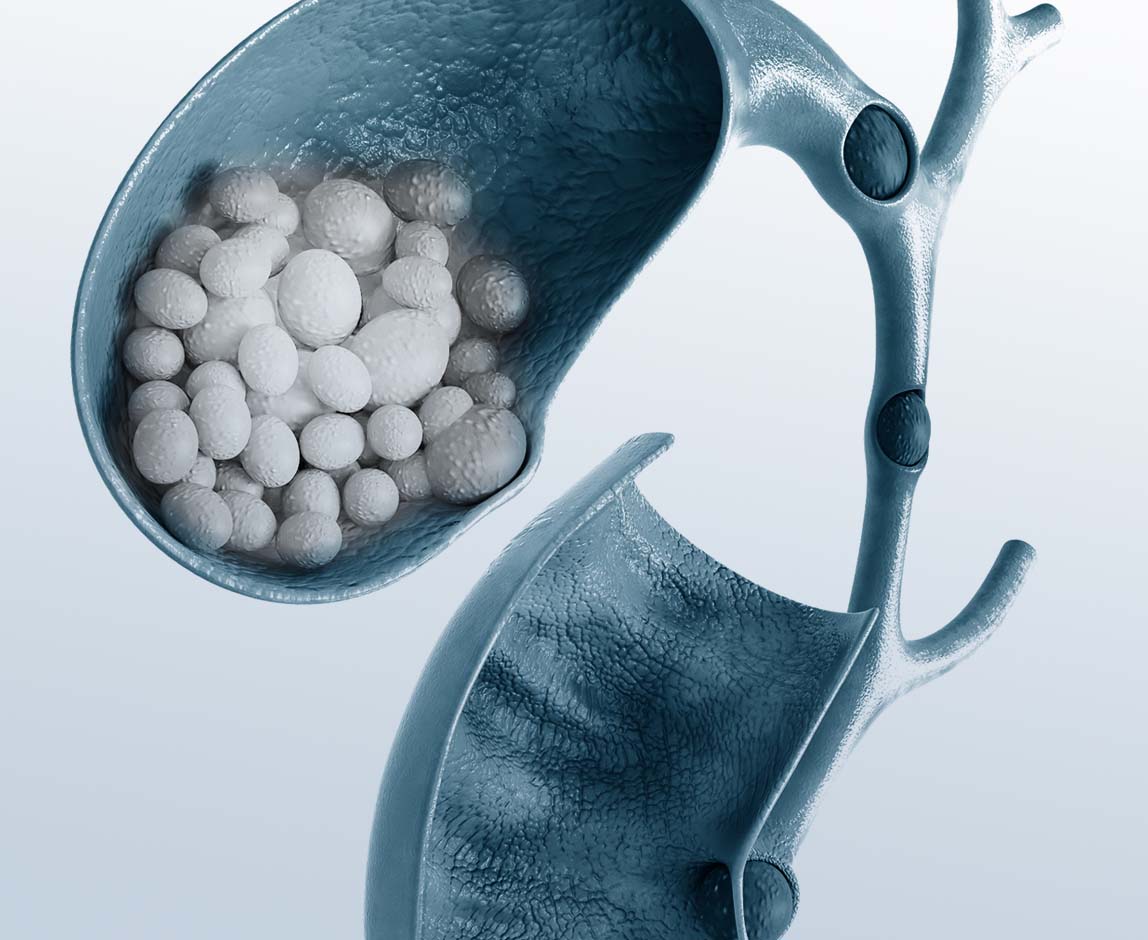
Normally, bile acids and proteins prevent the formation of stones. However, when there is an imbalance in the bile components, small pebble-like deposits called gallstones can form in the gallbladder.


- 1Cholecystitis
- Cholecystitis is the inflammation and/or infection of the gallbladder. It can be a sudden event as Acute Cholecystitis, or simmer and recur as Chronic Cholecystitis
- Gallbladder cancer is a risk of in patients with recurrent and longstanding chronic cholecystitis
- 2Obstructive jaundice
- When the gallstone drop out of the gallbladder, it can get stuck along common bile duct and this will cause the bile flow to be obstructed
- The build up of bile in the body will lead to jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin, tea-coloured urine, pale stools). Prolonged jaundice can lead to an impairment of liver function and infection
- 3Cholangitis
- If a gallstone gets stuck along the bile duct and obstruct bile flow. Other than jaundice, bacteria within the bile duct will overgrow, this can spread into the blood stream resulting in a potentially severe infection (Sepsis)
- 4Pancreatitis
- When the gallstone migrate and block the common channel where the pancreatic juices and the bile meet just before it drains into the small intestine, it can block the pancreas and cause inflammation of the pancreas, this may lead to more serious complications (Systemic inflammatory Response Syndrome or Multiorgan failure)
- Recurrent pancreatitis can simmer as Chronic pancreatitis and cause pain, pancreatic dysfunction and in the long term, as risk of pancreatic cancer
- 5Others
- Gallstone ileus, Liver abscess, Mirizzi's syndrome, Bile duct cancer
- Complicated gallbladder infection- Empyema(Pus), Perforation, Gangrene, Mucocele, Porcelain gallbladder, Gallbladder cancer
Patients over 40–50 years of age as compared to younger patients.
Women are twice as likely as men to develop gallstones due to higher oestrogen levels.
& Genetics
Gallstones tend to run in families, suggesting a genetic link.
Obesity is a major risk, and factors like comorbidities and a sedentary lifestyle all play a part.
A diet high in cholesterol and fat but low in fibre increases the risk of gallstone formation.
Diabetic patients have higher fatty acids. They also tend to experience more severe infections.
While statins lower blood cholesterol, they increase the amount of cholesterol secreted into the bile.
Patients on prolonged intravenous feeding, or with certain blood disorders, liver cirrhosis, and Crohn’s Disease.
Myth 1: Gallstones can be ‘flushed’ away
Myth 2: Gallstones can be broken up using shockwaves
Myth 3: Surgery for gallstones is risky and painful
Myth 4: You can’t eat normally or lead a normal life without a gallbladder
Myth 5: All gallstones should be treated
Myth 6: It is ok and better to just remove the gallstones alone
Gallbladder’s Role
conditions of the gallbladder.

#08-07, 3 Mount Elizabeth, Singapore 228510
| Tel | : 6454 0054 |
| : 9012 0054 |
#05-01, 6 Napier Road, Singapore 258499
| Tel | : 6471 0054 |
| Fax | : 6271 0054 |
| Mon to Fri | : 9am to 5pm |
| Sat | : 9am to 1pm |
| Sun & PH | : By Appointment Only |
